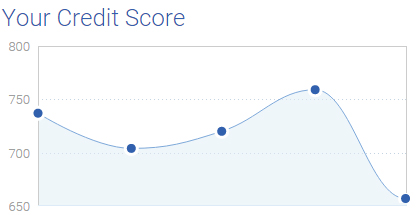
 The majority of consumers are not very familiar with how credit works and how credit scores are calculated.
The majority of consumers are not very familiar with how credit works and how credit scores are calculated. Multiple negative items can be removed off a consumer’s credit report but the real score issue becomes when a new negative account is reported.
New lates, new collections, new charged-off accounts are all considered new negative accounts and their impact on scores is tremendous.
How does a new negative account impact your credit scores?
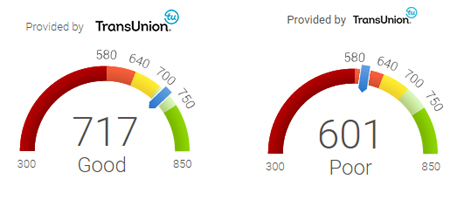
On the example above, this consumer had one single new negative item reported. It was a new medical collection account in the amount of $27. As seen above, the amount of a collection is irrelevant, as the system reads the new collection as risky behavior, regardless of amount owed. This specific consumer had an instant score drop of 116 points, even after multiple negative items were removed off his credit report.
A new derogatory mark is almost always to blame when anyone experiences a significant drop on scores. Tax liens, accounts going into collections and bankruptcies are among the most serious things that can happen to a credit score. Since they represent major delinquencies, they can reflect poorly on a consumer’s ability to take care of finances.
As a consumer goes through the credit repair process, multiple negative items are removed. Multiple negative items can be removed at once, but if the consumer keeps on having new negative items reported, the scores will not improve, furthermore, they will drop significantly.
Why are new negative accounts so difficult to remove?
New negative items are difficult to remove as the creditor most likely will have all the necessary documents in order to prove the account is the consumer’s. Since the negative item is new, all of the information regarding such account is fresh in their system. If the account is verifiable, it will not be removed.
 How can you avoid new negative accounts being reported?
How can you avoid new negative accounts being reported?Everyone gets notices in the mail and has a general idea of new unpaid debts. The key is to have these debts paid before they are reported to the credit report.
Most agencies wait 30 days before reporting a new collection to the credit report, but according to the Federal Trade Commission, a collection agency can opt to report the debt at any time after purchasing the account. This could mean the report would have a score drop sooner than thought. Therefore, it is imperative that the consumer acts quickly to pay the debt (even through an installment plan) and avoid credit consequences.
New credit card, auto loan, etc. lates can be avoided by keeping accounts current. The credit repair process cannot prevent new lates from being reported if a consumer’s current obligations are not being paid on time. A new 30-day late will be reported once a consumer has been 30 days late on an installment account. Student loans may report 90-day lates, but only after 2 unpaid billing cycles.
How about the negative impact of new inquiries?
Generally when anyone applies for a new form of credit, whether it’s a credit card, an auto loan or a mortgage, a hard inquiry is placed on the credit report. Normally, a single inquiry would initially only drop a few points off of the scores. However, if a consumer has applied for several accounts in a short period of time, he/she could appear desperate for credit and the damage from those hard inquiries might add up.
It is estimated that a credit report may only have up to 4 inquiries within a 2 year period before a new inquiry hurts its scores.
It is advisable to avoid getting the credit report pulled while a credit repair is in process. The scores will drop and the new inquiry will not be removed.
It is also advisable to loan officers to avoid running the consumer’s report multiple times as an attempt to getting him/her approved for the home loan. Each and every inquiry counts negatively towards the consumer’s score, regardless if they are all from the same company or if they are all within a specific timeframe.
How can your credit report recover?
Although all collection accounts are inherently negative, paid debt still looks better to lenders who review a consumer’s report than unpaid debt. The credit repair process will attempt to remove the new negative items but they can remain on a consumer’s credit report for seven years, regardless of it being paid or unpaid. Fortunately, the older an item is, the less impact it has on overall score. Hopefully the amount of negative items removed through the credit repair process will offset the damage caused by a new negative item reported. Provided the consumer manages his/her debts responsibly in the future, his/her credit scores will continue to recover with time.
Contact us for more details.
